Our Projects
Ongoing Initiatives
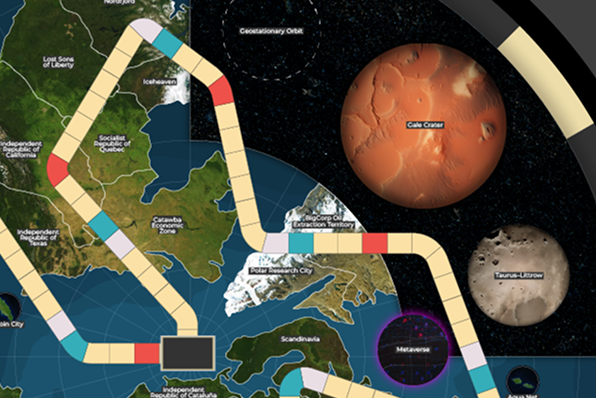
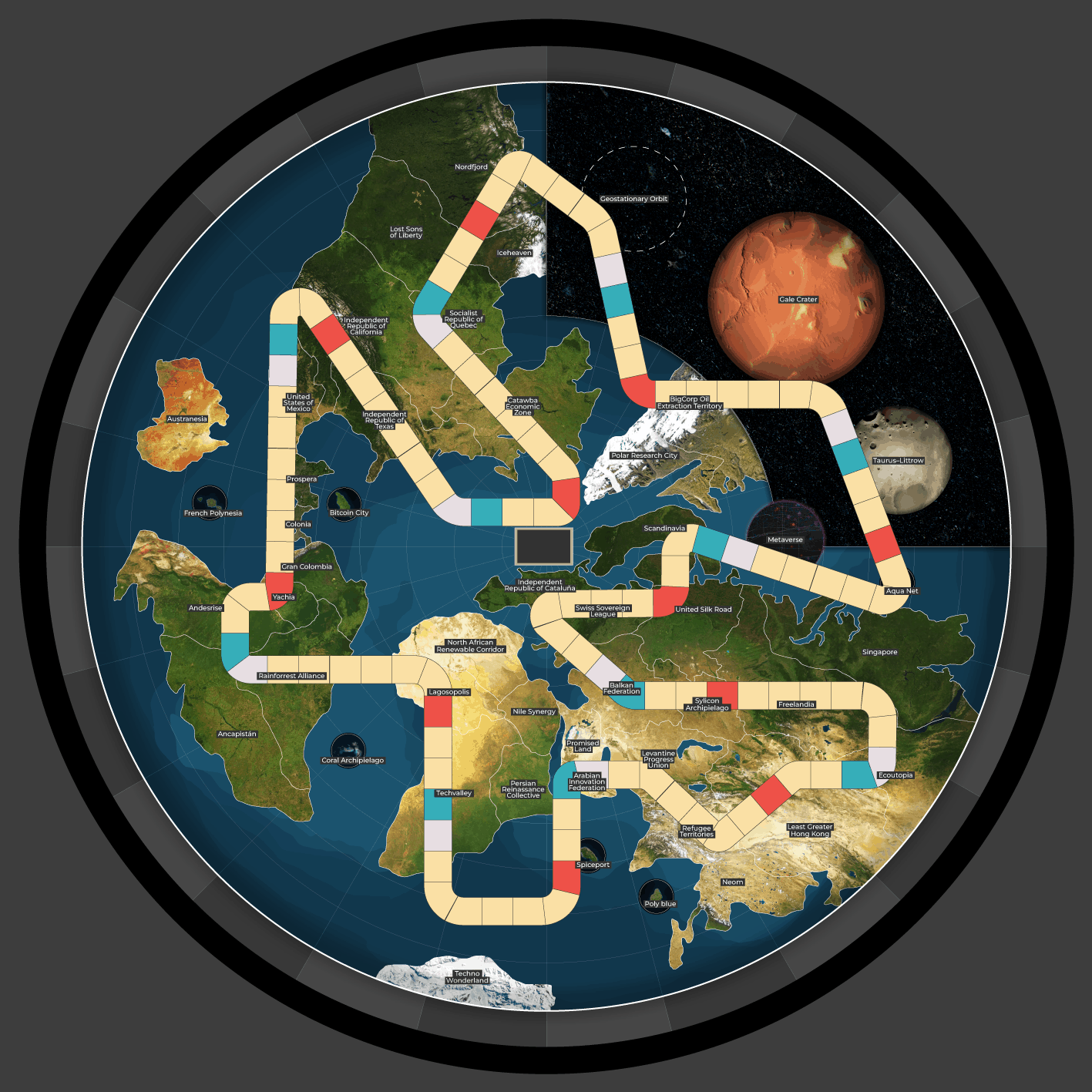
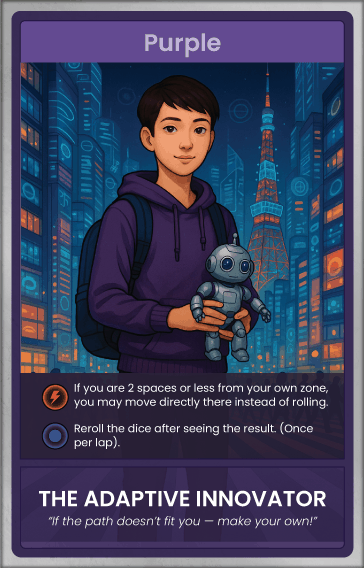
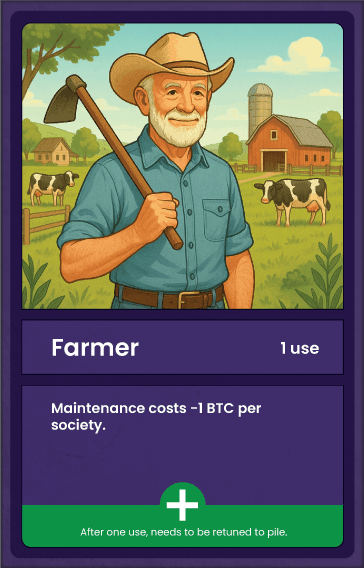
Startup Societies Boardgame
Most games feature nation building, tribes, civilizations, cities. This is the first Startup Society game where entrepreneurs build Special Economic Zones and other types of special jurisdictions.
Journal of Special Jurisdictions
The only academic journal in the world dedicated to the study of experimental forms of governance, Special Economic Zones, and special jurisdictions in general.
Startup Societies Network Café
A monthly gathering where innovators and pioneers in startup societies share insights, challenges, and strategies for building the future.


In brief
What is a Startup
Society?
A Startup Society is a small experiment in governance. Examples include Special Economic Zones, master-planned communities, smart cities, Charter Cities, DAOs, ecovillages, seasteads, Network States, SeaZones, Special Administrative Regions, blockchain-based jurisdictions, and other types of extraterritories. Startup Societies can be physical, legal or digital based–or all combined!
A geographically defined community that implements new governance models or social systems in a physical space. Examples include master-planned communities, ecovillages, smart cities, or seasteads.
A jurisdiction that operates within or alongside existing legal frameworks, often through special legal status within a host Nation. Examples include Special Economic Zones, Charter Cities, or Special Administrative Regions. These societies test new governance models via legal autonomy or regulatory innovation.
A community or governance network that exists primarily online, typically coordinated through blockchain technology, DAOs, or digital platforms. These emphasize decentralized governance, digital identity, and virtual citizenship.
world


Our Goals Mission
Help Us Decentralize
We empower pioneers to build the future of governance through Startup Societies—small-scale experiments in legal, physical, and digital systems. We support visionary entrepreneurs creating Special Economic Zones, Charter Cities, DAOs, Seasteads, and beyond.
We envision a world where Startup Societies flourish—decentralized, experimental governance models that empower communities with autonomy, innovation, and economic growth. Through global collaboration, cutting-edge research, and strategic partnerships, we are building a robust ecosystem that supports founders in launching, funding, and sustaining Startup Societies that reimagine how governance can work.
- Innovation & Experimentation – We embrace bold, new governance models and encourage continuous experimentation to discover better ways of organizing societies.
- Autonomy & Decentralization – We believe in empowering communities to govern themselves, free from excessive bureaucracy.
- Freedom of Choice & Mobility – Startup societies should compete for citizens by offering better opportunities and governance, ensuring individuals have the freedom to choose where they live and contribute.
- Technological Advancement – We prioritize leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance governance, infrastructure, and societal efficiency.
- Community & Collaboration – We foster global networks of entrepreneurs, investors, and visionaries.
- Sustainability & Resilience – We aim to build societies that are adaptable, economically sustainable, and capable of withstanding challenges through innovative resource management.
- Alternative Governance – We challenge outdated political and economic structures.
Our Idea is Simple
Don’t argue about it, Build the alternative

Why create a Startup Society?
Test bold ideas at a small scale, innovate without bureaucracy, and build governance from the ground up.

Governance
Innovation
Experiment with new legal, political, and regulatory frameworks to unlock better outcomes.

Real Estate
Innovation
Leverage private land, special zones, or virtual spaces to create thriving new communities.

Like-minded
Communities
Bring together people who share your values and vision for a better way to live and work.
Need expert support? Let’s build the future society together!
Just like business, Startups
Tend To Be
Small
Usually the size of a neighborhood or a city, although digital ones are deterritorialized.

Prosperous
Huge prosperity has been created from succesful startup societies.

Focused
Usually they center on a niche: sustainability, technology, automation, blockchain, freedom, walk ability, decentralization, tax incentives, regulatory incentives, VR, among others.

Data
Useful when they fail because they are able to provide data about how to improve and how not to.

Innovative / Experimental
Startup Societies venture into new areas of governance, producing localized reforms.

Responsive
Successful if listen to and/or adapt to their communities needs and environments.
Support our work. Make a Difference
Throughout history, small governments have driven progress and the economy–from the Hanseatic League to Venice in the middle ages, to Shenzhen and Dubai today. Today’s countries know it, and this reasoning is behind projects to create new cities, and SEZs.
Gatherings
Upcoming Events

Startup Societies Support Café #1 (Zoom)
Startup Societies Support Café #2 (Zoom)
Startup Societies Support Café #3 (Zoom)
Some Startup Societies Examples


Próspera, Honduras
Based on the Honduran ZEDE law, Próspera is an entirely new city that has its own civil law and regulatory structure, independent of that of Honduras, though it remains bound by the Honduran constitution and its criminal law code. Inspired by successful special economic zones such as Shenzhen in China or Dubai in the United Arab Emirates, Próspera intends to make it much easier for residents to interact with government services by better aligning local government incentives and residential needs.


Conceived and financed by the Walt Disney Company, Celebration is a master-planned community located near Walt Disney World. Though Disney divested control of the community, it still owns and operates many local services, including power utilities. Voting is restricted to landowning entities - with Disney remaining the largest such entity.


Catawba Digital Economic Zone
A pioneering initiative by the Catawba Indian Nation in the Carolinas. Established in 2022, the CDEZ is the first entirely virtual special economic zone (SEZ) in the United States, specifically offers a unique legal framework for digital assets, blockchain companies, and fintech ventures. Instead of physical infrastructure, the CDEZ enables remote business incorporation through “eCorporations.”


Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC)
The DIFC is self-governed financial and business district with its own legal system and business regulations aimed at attracting foriegn investment. Laws are issued in English, businesses can operate without a local partner, companies can take advantage of a 50-year guarantee of zero taxes on corporate income and profits.


Ethereum
Ethereum is the blockchain technology powering ether (ETH), the world's second- largest cryptocurrency, as well as thousands of decentralized application (dapps). Though it may be digital in nature, the Ethereum community has had huge impacts on the world at large.


Cayman Island
Enterpise City
Made up of three Special Economic Zones (SEZS), the Cayman Island Enterprise City aimed to attract tech and service-industries to setup a physical presence in the Cayman Islands with incentives such as a 100% exemption from income and sales tax, and renewable 5-year work/residency visas that can be obtained in as little as 5 working days. As of 2020, the economic impact is estimated at over $500 million, and more than 250 companies are currently















Our Academic Journal
The only academic journal in the world dedicated to the study of small, experimental forms for governance.

Dec 31, 2024
Issue V, with papers about: Constitutional, Economic, and Networked Perspectives on Special Jurisdictions (2024)

Dec 30, 2023
Issue IV, with papers about: Market Institutions, Private Governance, and the Future of Special Jurisdictions (2023)

Oct 27, 2022
Issue III, with papers about: Experimental Zones and Institutional Adaptation in the United States and a Fragmented World (2022)








A better governed world starts with your donation
The Startup Societies Foundation (SSF) promotes new city creation and decentralized governance through research, collaboration, and events, integrating blockchain, special jurisdictions, and new communities.
Next events
Startup Societies Support Café #1 (Zoom)
Startup Societies Support Café #2 (Zoom)
Startup Societies Support Café #3 (Zoom)
Contact Us
United States
Mon – Fri: 9:00 am – 6:30 pm